Each of these can vary depending on the type of business created, and they may also vary from state to state. A sole trader or proprietorship is the most straightforward business structure. It’s operated by individuals for their benefit, and they don’t need to share their profits with others. $600 is to be considered a withdrawal because only $300 (1/3rd) is related to business and the other $600 was for domestic purpose. If the company needs money, the owners can either lend money to the company or invest more money by purchases more stock or a great ownership percentage. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
Understanding Business Entity Concept in Accounting: Definition, Examples, and Importance
The Conceptual Framework refers to a ‘reporting entity’ which is an entity that is required, or chooses, to prepare financial statements. The concept of a business entity is essential for anyone starting a business as it helps them define their legal and operational structure. Understanding the different types of business entities can help business owners choose the most suitable option for their company. The choice of business entity can affect various aspects of the business such as taxes, liability, ownership, and governance.
What is the relationship between owners and business entities?
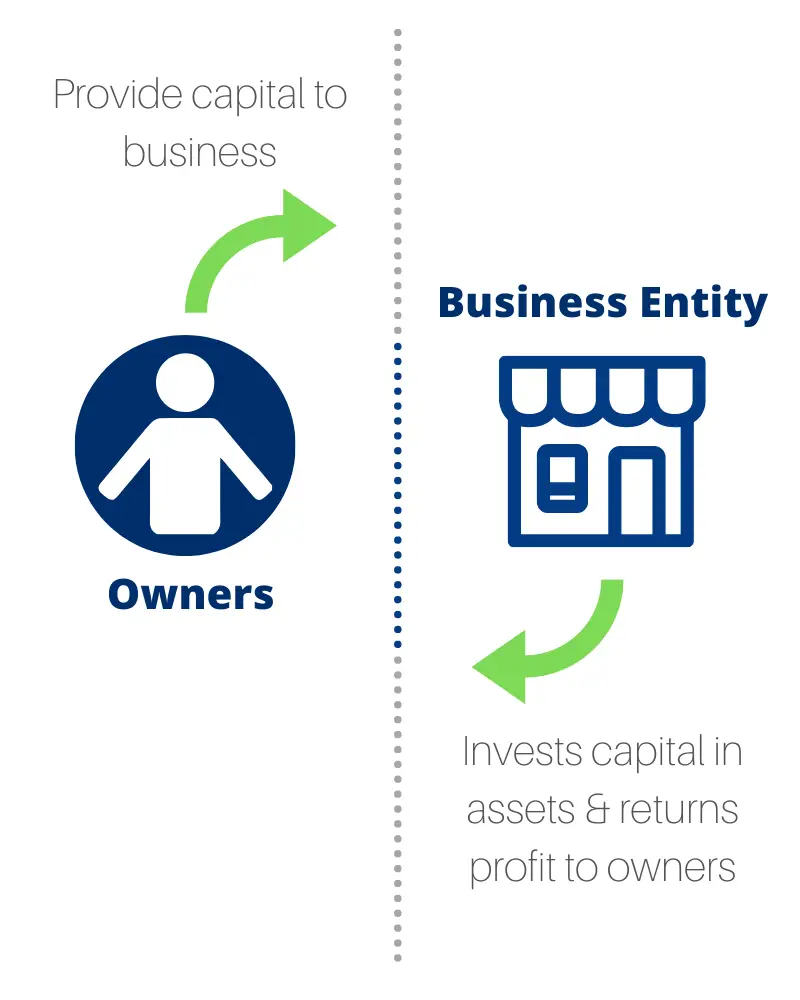
A business entity in accounting encompasses a wide spectrum of individuals and organizations. It encompasses the proprietors in the case of a sole proprietorship, the partners in a partnership firm, and the stakeholders in a corporation. Alternatively, a one-member business could be treated as a separate entity. If the owner of the business chooses to go that route, they will have to fill out a Form 8832 to declare an Entity Classification Election and file the form with the IRS. Unless the owner of the sole proprietorship or single-person LLC files the Form 8832 for their business, that business entity will fall into the default classification of a disregarded entity.
Business Entity Principle
The business entity concept is extremely important for business owners for several reasons described below. In transactions between businesses, it is common for payment not to be made on the same date that an order is made or that goods are transferred. You have two options, either as a C corporation or pass-through entity on taxes. The types of business entities mentioned above are just a few examples available to entrepreneurs who wish to start their businesses.
It includes the owners, managers, and workers or employees that contribute to making a profit for the company. Although the owners have a very important role as members owning a part of a business entity, their activities generally do not contribute to making profit and loss. Therefore, those activities are not relevant for the purpose of accounting information about the business itself. In relation to corporations, the business entity concept first arose in the form of the historical legal decision in England in the case of Salomon vs Salomon & Co (1897) A.C 22.
How is the business entity different from its owners?
Equally, preparers should not be ‘overly prudent’ to the extent that they pick the lowest possible outcome simply to avoid the risk of overstating assets and income or understating liabilities and expenses. This would still not provide a fair presentation of the financial position or financial double declining balance method: a depreciation guide performance of the entity and, therefore, it is important that caution is exercised to avoid this as well. If the transactions are not recorded in a mixed manner (involving both business and business owners in one statement) it will make the accounting information less usable.
- The economic entity assumption does not always apply to a legal entity.
- The budget created for the company reflects the firm’s value, not the owner’s net worth.
- Apart from the owners, the business entity concept applies to subsidiaries of the same group as well.
- The business entity principle focuses on financial separation, not legal liability.
The business entity concept has a wide range of use across many industry sectors, particularly accounting. With the separate entity concept, you are shielded from the risk of disrupted cash flows due to the overwhelming cost of paying all your taxes together. This article will teach the business entity concept to help you accurately account for your business profits.
Whenever a financial transaction occurs for both, it should be allocated properly. A separate legal entity is one that has rights and responsibilities different from its members such as owning assets, entering into contracts, and incurring liabilities. By contrast, in joint-stock companies, the concept is fully followed.
In other words, an investor can see if the business has good cash flow from it’s profitable operations or because the owner keeps funding the business with owner contributions. With the business entity concept not providing cover in the event of legal issues, the owner is left to fend for himself when such a situation arises. Another example is a business owner with two different credit cards, one for his business and the other solely for personal use.
